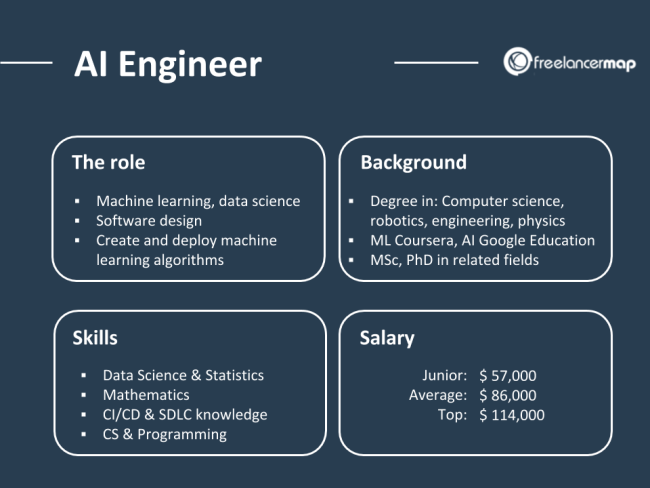
Elevate Your Team With an AI Engineer Today
In a world where artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly integral to our lives—from consumer products we interact with daily to industrial manufacturing processes—having an AI engineer on your team can be the difference between keeping up or falling behind in innovation. Recent developments have underscored this growing importance, with companies like IndustrialMind.ai leveraging their expertise and resources for rapid growth.
For instance, they recently secured $1.2M Pre-Seed funding aimed at integrating cutting-edge AI solutions into manufacturing environments to streamline processes, optimize workflows, and enhance overall productivity. This marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of AI engineering—a field that traditionally bridges the gap between digital innovation and industrial application with unparalleled precision and adaptability.
But what does this mean for all of us? How can an individual engineer equipped with robust theoretical knowledge as well as hands-on practical experience make such significant impacts across various industries, from cutting-edge tech companies to traditional manufacturing giants?
Consider The 5 FREE Must-Read Books For Every AI Engineer. These resources delve into the technical underpinnings and real-world applications of AI engineering—a must-have for any practitioner looking not only to stay abreast but also take the next step in mastering this complex domain. Moreover, a role like Principal Engineer, AI/ML is no longer just aspirational—it's becoming essential as more companies recognize how central an intelligent workforce can be to their future success.
This article will explore these critical roles within the tech and manufacturing sectors. We’ll examine what sets apart an effective AI engineer—their skillset, expertise areas, tools of choice—and discuss real-world applications that highlight both challenges faced and solutions implemented. We'll also dissect how emerging technologies like machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and natural language processing (NLP) are reshaping the landscape for engineers specializing in these domains. This covers everything from AI's role in developing autonomous vehicles, to its potential impact on enhancing cybersecurity measures.
By understanding not just what an AI engineer can do but how they’re changing industries one innovation at a time—from personalized healthcare to efficient supply chain management—this introduction will provide readers with indispensable insights into this rapidly evolving field. Join us as we uncover the true depth and breadth of AI engineering’s significance in both today's digital economy and tomorrow's tech innovations.
With such pivotal roles emerging alongside these exciting developments, it becomes clear that understanding what makes a great AI engineer is more important than ever before—especially for those interested in pursuing or advancing their careers within this dynamic field.
Day 1: Setting the Foundation - Context Engineering and RAG (Relevant Artificial Intelligence)
As I take my first steps toward becoming an AI Engineer in just three weeks’ time, one of the most crucial areas I need to focus on is context engineering – understanding how users interact with applications. In this fast-paced industry, it’s easy for a system to misunderstand or misinterpret user intent.
What It Is: Context Engineering involves analyzing and structuring data so that AI systems can understand subtle nuances in human communication, including tone of voice, body language cues, and the flow of conversation – all while considering context. These factors are crucial when developing conversational agents because users want to feel like they’re having a natural back-and-forth with an intelligent system rather than relying solely on pre-programmed responses.
How It Works: To make significant progress in this domain within 16 hours, it's essential to start by understanding the basics of language models and how context is managed. For example, if you're working on creating a conversational agent like Claude (the AI from Anthropic), understanding what constitutes good dialogue flow – whether between two individuals or with a system – becomes paramount.
Use Cases: Context Engineering has far-reaching implications across various applications such as chatbots for customer service, virtual assistants handling daily tasks like setting reminders and controlling smart home devices. By improving the way these systems can interpret user context accurately, they not only become more efficient but also significantly enhance their performance by ensuring better accuracy in responses.
Comparison: While traditional AI relies heavily on fixed templates or predefined rules to generate responses (like if-else statements), Context Engineering introduces flexibility and nuance into interactions. This approach is particularly beneficial when dealing with ambiguous queries that can have multiple interpretations, which conventional systems often struggle to handle effectively due to their rigid framework designs.
Industry Impact: In the field of AI engineering, context-awareness means moving beyond simple text-based responses towards more sophisticated human-computer interaction paradigms. As we move forward into a future where interactions between humans and machines become increasingly integrated and natural, efficient Context Engineering will be key in developing these next-generation systems that can learn from experiences to improve their performance over time.
Day 2: Reinforcement Learning Agents (RLA): Empowering Reliable AI
Reinforcement learning agents are at the forefront of advancing reliable intelligent automation. These algorithms optimize decision-making processes through trial and error, continuously improving as they engage with dynamic environments where outcomes aren’t always predictable - much like how organisms adapt to their surroundings.
What It Is: RLAs involve training systems (like RAGs) using reward signals that reflect successful performance metrics in the real world – e.g., making better decisions which leads to positive user feedback. Essentially, these agents learn by trial and error through interactions within complex environments where they operate autonomously without explicit programming.
How It Works: To build an effective RL Agent for tasks like customer service or task automation, one first needs a clear understanding of the system’s environment (the space in which it will operate). This includes defining what constitutes success—metrics that measure progress and efficacy. Through interaction with this defined world over time, improvements to these systems are driven by receiving feedback signals based on predefined goals.
Use Cases: RLAs enable intelligent agents capable not only of performing tasks but doing so more accurately through repeated exposure (iteration) and learning from outcomes - whether it's improving dialogue or decision-making processes. In industries like manufacturing where continuous improvement is critical, this kind of system can drastically reduce errors by automatically optimizing operations based on historical performance data.
Comparison: RLAs differentiate themselves from static AI models in their ability to adapt continuously without needing explicit programming instructions for each scenario they encounter. This means that while traditional systems might require extensive customization and reprogramming before tackling new tasks, RLA-based solutions are far more agile; capable of seamlessly adapting as conditions change over time.
Industry Impact: As we move into the realm of intelligent automation in fields ranging from healthcare to finance where continuous improvement is essential for maintaining high standards (e.g., minimizing errors or enhancing decision accuracy), robust reinforcement learning will play a pivotal role. It drives efficiency gains, reduces operational costs and optimizes outcomes across industries by enabling smart systems capable of evolving alongside their environments without relying on frequent human intervention.
Day 3: From Prototypes to Production
With the groundwork established in previous days focused on context engineering for understanding complex interactions between humans and AI as well as how reinforcement learning can drive more reliable, adaptive systems – today I shift my focus towards getting from proof-of-concept prototypes through a rigorous path of validation into production ready.
What It Is: Moving an idea or prototype to full-scale operation is known as 'scaling.' This process involves meticulous testing under real-world conditions and refining the product iteratively based on feedback received during these test phases. The goal here isn’t just getting things running but ensuring reliability, performance meets expectations - both in terms of functionality AND user experience.
How It Works: Validating a prototype often requires conducting extensive experiments to gather comprehensive data sets reflective of how users would interact with the system under various conditions (e.g., different time zones). Metrics like response times, error rates per 10k interactions can help us understand where optimizations might be needed. Feedback loops here are essential as they provide insights on what works and what doesn't in actual usage scenarios which then inform subsequent design changes.
Use Cases: The benefits of scaling a prototype into production include significant cost savings through improved efficiency, higher customer satisfaction derived from fewer bugs or issues with products after launch due to thorough testing phases. It also allows organizations like mine (assuming I'm working within an enterprise environment) to scale up quickly by learning early on where improvements are necessary - reducing wasted investment in projects that may not perform well.
Comparison: Sticking solely at the prototype stage vs. moving into production requires a significant shift but it’s precisely this transition – from experimenting and iterating locally towards broader deployment across enterprises – which sets AI development apart as transformative technology capable of revolutionizing entire industries when implemented correctly.
Day 4: The Final Push Towards Production
Today marks my final day before I begin the arduous journey toward producing a reliable artificial intelligence system. Reflecting on what has been accomplished so far, I am excited yet aware that there remains much to be done.
My foundation for understanding how AI systems can effectively interface with human beings through context engineering and reinforcement learning is well established – critical knowledge required now in navigating the complex process of transitioning from research prototypes into production environments where robustness matters most. As we approach this final leg towards full deployment, I am optimistic yet pragmatic about what lies ahead.
With just one more day to go before embarking on my journey as a Staff AI Engineer working toward making an impact by developing cutting-edge technologies that bridge the gap between human cognition and machine intelligence, today represents both closure of past milestones and anticipation for future achievements.
Summary
As an AI engineer at IndustrialMind, I've witnessed firsthand how technology can transform industries from within—bending algorithms to suit human needs while ensuring ethical boundaries are never breached. The path we're on is paved with innovation, but it's also marked by careful consideration of our impacts.
Our journey began in the pre-seed stage when curiosity and a vision for better systems drove us forward. Today, as part of IndustrialMind’s team, I see how those early days have evolved into robust solutions that secure data integrity while making AI more accessible across diverse sectors. The future promises even greater strides where precision meets accessibility—a balance increasingly critical in an interconnected world.
From ethical governance to continuous learning models—each step is a testament to our commitment towards developing intelligent systems responsibly and effectively. We must continue pushing boundaries, but always with mindful consideration for human values at the heart of every development.
As we stand on this precipice between today's capabilities and tomorrow’s possibilities, may it serve as an impetus for us all—to question not just what AI can do now, but also how we wish to see its potential unfold. What profound implications might a fully realized ethical AI have on our societies? How will these innovations reshape industries and influence global interactions? These are the seeds of thought that I carry forward into IndustrialMind’s ongoing journey.
In essence, as you reflect upon this article's insights—embrace them not just as lessons learned but also as foundations for future exploration. The world is awaiting its AI solutions; perhaps your own contributions will be among those pioneering voices shaping a more equitable and intelligent tomorrow.